Anti-p63a mouse monoclonal, 100 ul, Species x-Reactivity: human, Applications: IHC
Cat#: BSH-7449-100 100ul, BSH-7449-1 1ml, BSH-7449-RTU 7ml
Clone: BS63
S/R: human
Application: IHC
The p63 gene is a homologue of the p53 tumor suppressor gene. Like p53, p63 contains a transactivation (TA) domain induce the transcription of target genes, a DNA binding domain, and an oligomerization domain (OD), used to form tetramers. In contrast to p53, the p63 gene encodes for at least six major isotypes. Three isotypes (TAp63α, TAp63β, and TAp63γ) contain the transactivating (TA) domain and are able to transactivate p53 report genes and induce apoptosis. In contrast, the other three isotypes (ΔNp63α, ΔNp63β, ΔNp63γ) are transcribed from an internal promoter localized within intron3, lack the TA domain, and act as dominant-negatives to suppress transactivation by both p53 and TAp63 isotypes. p63 is highly expressed in the basal cells of the epithelium significant for proper limb outgrowth and morphogenesis.4 In differentiating tissues, p63 is crucial for maintaining the stem cell identity of the basal cells, and is indispensable for correct development of the skin as well as the limb. p63-deficient mice lack all squamous epithelia and their derivatives, including hair, whiskers, teeth, as well as mammary, lacrimal, and salivary glands.Tissue specificity: Widely expressed, notably in heart, kidney, placenta, prostate, skeletal muscle, testis and thymus, although the precise isoform varies according to tissue type. Progenitor cell layers of skin, breast, eye and prostate express high levels of DeltaN-type isoforms. Isoform 10 is predominantly expressed in skin squamous cell carcinomas, but not in normal skin tissues.
 |
 |
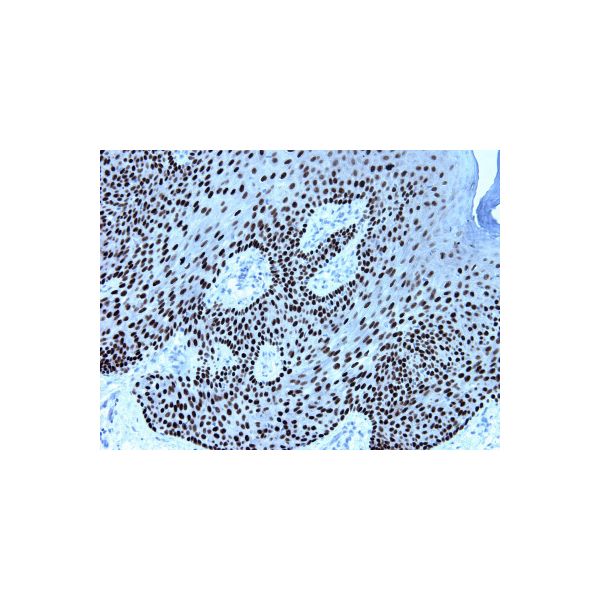
| Human tonsil has been stained using P63a antibody P63a is basal cell marker in squamous epithelial. p63 is a very useful marker for squamous, myoepithelial and urothelial neoplasm. | Human skin epidermis has been stained. P63a is basal cell marker in squamous epithelial. p63 is a ry useful marker for squamous, myoepithelial and urothelial neoplasm. |
| Price | 1.155,00 RON (preturile sunt fara TVA) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Description |
Cat#: BSH-7449-100 100ul, BSH-7449-1 1ml, BSH-7449-RTU 7ml The p63 gene is a homologue of the p53 tumor suppressor gene. Like p53, p63 contains a transactivation (TA) domain induce the transcription of target genes, a DNA binding domain, and an oligomerization domain (OD), used to form tetramers. In contrast to p53, the p63 gene encodes for at least six major isotypes. Three isotypes (TAp63α, TAp63β, and TAp63γ) contain the transactivating (TA) domain and are able to transactivate p53 report genes and induce apoptosis. In contrast, the other three isotypes (ΔNp63α, ΔNp63β, ΔNp63γ) are transcribed from an internal promoter localized within intron3, lack the TA domain, and act as dominant-negatives to suppress transactivation by both p53 and TAp63 isotypes. p63 is highly expressed in the basal cells of the epithelium significant for proper limb outgrowth and morphogenesis.4 In differentiating tissues, p63 is crucial for maintaining the stem cell identity of the basal cells, and is indispensable for correct development of the skin as well as the limb. p63-deficient mice lack all squamous epithelia and their derivatives, including hair, whiskers, teeth, as well as mammary, lacrimal, and salivary glands.Tissue specificity: Widely expressed, notably in heart, kidney, placenta, prostate, skeletal muscle, testis and thymus, although the precise isoform varies according to tissue type. Progenitor cell layers of skin, breast, eye and prostate express high levels of DeltaN-type isoforms. Isoform 10 is predominantly expressed in skin squamous cell carcinomas, but not in normal skin tissues.
|

 English
English