S9153S, BG-Maleimide - 2 mg
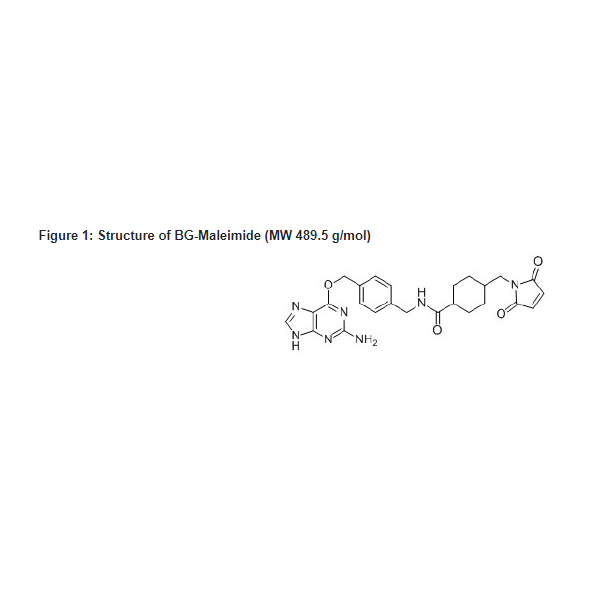
BG-Maleimide is a thiol-reactive building block for the one-step synthesis of SNAP-tag® substrates from thiol-containing precursors such as thiol-modified oligonucleotides.
BG-Maleimide is a thiol-reactive building block for the one-step synthesis of SNAP-tag® substrates from thiol-containing precursors such as thiol-modified oligonucleotides.
This building block allows you to make custom SNAP-tag substrates for labeling SNAP-tag fusion proteins for a wide range of applications
It can be used for the coupling of proteins and solid surfaces such as DNA chips
The SNAP-tag protein labeling system enables the specific, covalent attachment of virtually any molecule to a protein of interest. The SNAP-tag is a protein based on human O6-alkylguanine-DNA-alkyltransferase (hAGT). SNAP-tag substrates are fluorophores, biotin or beads conjugated to guanine or chloropyrimidine leaving groups via a benzyl linker. In the labeling reaction, the substituted benzyl group of the substrate is covalently attached to the SNAP-tag.
There are two steps to using this system: sub-cloning and expression of the protein of interest as a SNAP-tag fusion, and labeling of the fusion with the SNAP-tag substrate of choice. Expression of SNAP-tag fusion proteins is described in the documentation supplied with SNAP-tag plasmids.
| Price | 2.910,00 RON (preturile sunt fara TVA) |
|---|---|
| Description |
BG-Maleimide is a thiol-reactive building block for the one-step synthesis of SNAP-tag® substrates from thiol-containing precursors such as thiol-modified oligonucleotides. This building block allows you to make custom SNAP-tag substrates for labeling SNAP-tag fusion proteins for a wide range of applications The SNAP-tag protein labeling system enables the specific, covalent attachment of virtually any molecule to a protein of interest. The SNAP-tag is a protein based on human O6-alkylguanine-DNA-alkyltransferase (hAGT). SNAP-tag substrates are fluorophores, biotin or beads conjugated to guanine or chloropyrimidine leaving groups via a benzyl linker. In the labeling reaction, the substituted benzyl group of the substrate is covalently attached to the SNAP-tag. There are two steps to using this system: sub-cloning and expression of the protein of interest as a SNAP-tag fusion, and labeling of the fusion with the SNAP-tag substrate of choice. Expression of SNAP-tag fusion proteins is described in the documentation supplied with SNAP-tag plasmids. |

 English
English