N9183S, pSNAPf Vector - 20 µg
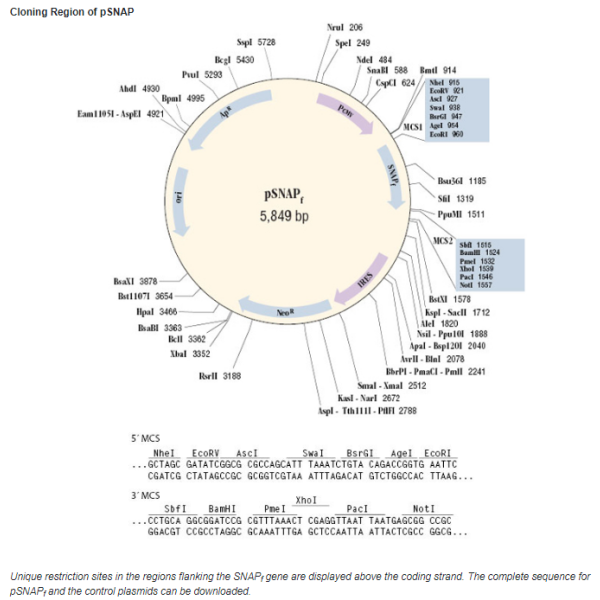
pSNAPf Vector is a mammalian expression plasmid intended for the cloning and stable or transient expression of SNAP-tag® protein fusions in mammalian cells. This plasmid encodes SNAPf, a SNAP-tag protein, which is expressed under control of the CMV promoter. The expression vector has an IRES (internal ribosome entry site) and a neomycin resistance gene downstream of the SNAPf for the efficient selection of stable transfectants. pSNAPf Vector contains two multiple cloning sites to allow cloning of the fusion partner as a fusion to the N- or C-terminus of the SNAPf.
pSNAPf Vector is a mammalian expression plasmid intended for the cloning and stable or transient expression of SNAP-tag® protein fusions in mammalian cells. This plasmid encodes SNAPf, a SNAP-tag protein, which is expressed under control of the CMV promoter. The expression vector has an IRES (internal ribosome entry site) and a neomycin resistance gene downstream of the SNAPf for the efficient selection of stable transfectants. pSNAPf Vector contains two multiple cloning sites to allow cloning of the fusion partner as a fusion to the N- or C-terminus of the SNAPf.
The SNAP-tag is a novel tool for protein research, allowing the specific, covalent attachment of virtually any molecule to a protein of interest. The SNAP-tag is a small protein based on mammalian O6-alkylguanine-DNA-alkyltransferase (AGT). SNAP-tag substrates are derivatives of benzyl purines and benzyl pyrimidines. In the labeling reaction, the substituted benzyl group of the substrate is covalently attached to the SNAP-tag.
pSNAPf contains an improved version of SNAP-tag, termed SNAPf. SNAPf displays faster kinetics in in vitro labeling and fast, specific and efficient labeling in live and fixed cell applications, thereby rendering it a desired research tool for analysis of protein dynamics.
There are two steps to using this system: sub cloning and expression of the protein of interest as a SNAPf fusion, and labeling of the fusion with the SNAP-tag substrate of choice. Cloning and expression of SNAPf fusion proteins are described in this document. The labeling of the fusion proteins with SNAP-tag substrates is described in the instructions supplied with the SNAP-tag substrates.
| Price | 1.200,00 RON (preturile sunt fara TVA) |
|---|---|
| Description |
pSNAPf Vector is a mammalian expression plasmid intended for the cloning and stable or transient expression of SNAP-tag® protein fusions in mammalian cells. This plasmid encodes SNAPf, a SNAP-tag protein, which is expressed under control of the CMV promoter. The expression vector has an IRES (internal ribosome entry site) and a neomycin resistance gene downstream of the SNAPf for the efficient selection of stable transfectants. pSNAPf Vector contains two multiple cloning sites to allow cloning of the fusion partner as a fusion to the N- or C-terminus of the SNAPf. There are two steps to using this system: sub cloning and expression of the protein of interest as a SNAPf fusion, and labeling of the fusion with the SNAP-tag substrate of choice. Cloning and expression of SNAPf fusion proteins are described in this document. The labeling of the fusion proteins with SNAP-tag substrates is described in the instructions supplied with the SNAP-tag substrates.
|

 English
English